What is triangular tube sheet?
A triangular tube sheet refers to a component used in heat exchangers and boilers. It is a plate-like structure with a triangular pattern of holes or tubes through which fluid flows. The tube sheet is typically made of a metal such as carbon steel, stainless steel, or copper alloys.
The triangular tube sheet design is advantageous in certain applications because it allows for increased fluid flow and heat transfer efficiency compared to other tube sheet designs. The triangular pattern of holes or tubes helps to create turbulence in the fluid, which enhances heat transfer by promoting better mixing and reducing the formation of boundary layers.
Triangular tube sheet material:
The material selection for triangular tube sheets depends on the specific application and the operating conditions of the heat exchanger or boiler. Here are some commonly used materials for tube sheets:
1. Carbon steel: Carbon steel is a cost-effective option that offers good strength and corrosion resistance. It is suitable for applications where moderate temperatures and non-corrosive fluids are involved.
2. Stainless steel: Stainless steel tube sheets are chosen when corrosion resistance is crucial, especially in applications involving corrosive fluids or high-temperature environments. Different grades of stainless steel, such as 304, 316, or duplex stainless steels, can be utilized based on the specific requirements.
3. Copper alloys: Copper-based alloys like brass and admiralty brass are often used in heat exchangers that involve seawater or other corrosive environments. These alloys provide excellent corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity.
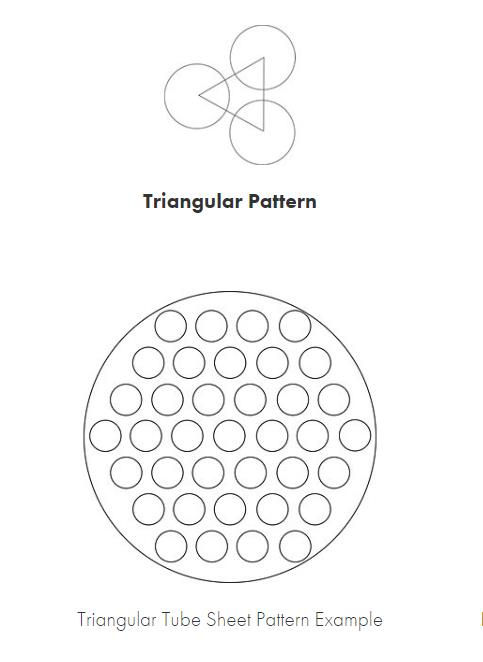
Triangular tube sheet size:
The size of the triangular tube sheet depends on several factors, including the number and size of the tubes or holes, the design pressure, and the required mechanical strength. The dimensions of the tube sheet are determined based on engineering calculations and considerations.
The tube sheet thickness is typically selected to ensure structural integrity and prevent tube-to-tube sheet joint failures. The thickness is determined by considering factors such as the tube material, tube sheet material, tube sheet diameter, tube pitch, operating pressure, and applicable design codes and standards.
Additionally, the size and arrangement of the tubes or holes in the tube sheet are crucial for efficient heat transfer and fluid flow. The diameter or size of the tubes and the spacing between them are selected based on heat transfer requirements, fluid properties, and pressure drop considerations.
Triangular tube sheet usages:
These tube sheets are commonly used in shell and tube heat exchangers, where they serve as the support and sealing element for the tubes. The tubes are inserted into the holes of the tube sheet and mechanically secured or welded in place. The triangular configuration provides structural integrity and ensures a tight seal between the tubes and the tube sheet.
The design of triangular tube sheets can vary based on the specific requirements of the heat exchanger or boiler. Factors such as the fluid type, pressure, temperature, and flow rate determine the material selection and thickness of the tube sheet.
Overall, triangular tube sheets play a critical role in facilitating efficient heat transfer in various industrial processes where heat exchange between two fluids is required.
Address :
Jl. K.H. Zaenal Mustafa No. 17
Jatinegara Jakarta Timur 13350
Phone : 62 21 8561234 ( Hunting )
Fax : 62 21 8513109
E mail : info@fintubes.co.id